# JSTL与EL表达式
[TOC]
## 导学
在之前的学习中,我们发现虽然可以在Jsp中使用Java语言,但是HTML和Java的结合好像不是那么紧密,而且操作HTML元素好像也不是那么方便。那么有没有一种简单的方式,来获取值并操作HTML元素呢?
## EL表达式
EL表达式是一种非常简单的数据表达方式,EL(Expression Language)表达式语言的出现就是为了简化JSP的输出。在早期的Jsp中,没有EL表达式,所有的程序都要使用out对象来一行行的输出。
语法:
~~~
${表达式}
~~~
实例:
~~~
public class Student {
private String name;
private String mobile;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getMobile() {
return mobile;
}
public void setMobile(String mobile) {
this.mobile = mobile;
}
public String toString() {
return name + ":" + mobile;
}
}
~~~
~~~
@WebServlet("/info")
public class StudentServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public StudentServlet() {
super();
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
Student stu = new Student();
stu.setName("子墨");
stu.setMobile(null);
String grade = "A";
request.setAttribute("grade", grade);
request.setAttribute("stu", stu);
request.getRequestDispatcher("/info.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
}
~~~
~~~
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8" import = "com.dodoke.el.Student"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
Student stu = (Student)request.getAttribute("student");
String grade = (String)request.getAttribute("grade");
out.println("<h1>姓名:" + stu.getName() + "</h1>");
out.println("<h2>手机:" + stu.getMobile() + "</h2>");
out.println("<h2>评级:" + grade + "</h2>");
%>
</body>
</html>
~~~
EL表达式版
~~~
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>姓名:${requestScope.student.name }</h1>
<h2>手机:${requestScope.student.mobile }</h2>
<h2>评级:${requestScope.grade }</h2>
</body>
</html>
~~~
通过以上的例子,我们可以看出EL表达式的应用非常简单,而且还不需要导入要使用的类,下面我们就来看看EL表达式的使用细节。
### EL的作用域对象
EL表达式包含四种不同的作用域:
* pageScope:从当前页面取值
* requestScope:从当前请求中获取属性值
* sessionScope:从当前会话中获取属性值
* applicationScope:从当前应用获取全局属性值
这四种作用域,作用范围从小到大,而且这四种作用域也对应了我们四种取值范围。当我们忽略书写这四种作用域时,el表达式将按作用域从小到大的顺序依次尝试获取。
~~~
@WebServlet("/info")
public class StudentServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public StudentServlet() {
super();
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
Student stu = new Student();
stu.setName("子墨");
stu.setMobile(null);
String grade = "A";
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
session.setAttribute("grade", grade);
session.setAttribute("stu", stu);
//request.setAttribute("grade", grade);
//request.setAttribute("stu", stu);
request.getRequestDispatcher("/info.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
}
~~~
~~~
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>姓名:${sessionScope.student.name }</h1>
<h2>手机:${sessionScope.student.mobile }</h2>
<h2>评级:${sessionScope.grade }</h2>
</body>
</html>
~~~
问:代码修改为这样以后该如何,得到的结果是多少?
~~~
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
Student stu = new Student();
stu.setName("子墨");
stu.setMobile(null);
String grade = "A";
request.setAttribute("grade","B");
request.getServletContext().setAttribute("grade","C");
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
session.setAttribute("grade", grade);
session.setAttribute("stu", stu);
//request.setAttribute("grade", grade);
//request.setAttribute("stu", stu);
request.getRequestDispatcher("/info.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
~~~
### EL表达式输出
语法:
~~~
${[作用域].属性名.[子属性名]}
~~~
el表达式支持将运算结果输出,也支持绝大多数对象的输出,本质是执行toString方法,也就是我们可以尝试重写toString方法,输出对象的信息。

### 输出参数
要求:查找并总结getParameter()方法和getAttribute()方法的区别
在Servlet中我们可以通过getParameter()方法来实现获取前端浏览器的参数,那么如何使用el表达式来接收其他页面传递的参数呢?
EL表达式内置param对象来简化参数的输出,它的语法:
~~~
${param.参数名}
~~~
~~~
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>姓名:${sessionScope.student.name }</h1>
<h2>手机:${sessionScope.student.mobile }</h2>
<h2>${param.teacher}</h2>
<h2>评级:${sessionScope.grade }</h2>
</body>
</html>
~~~
## JSTL标签库
* JSTL(JSP Standard Tag Library),JSP标准标签库
* JSTL用于简化JSP开发,提高代码的可读性和可维护性
* JSTL由SUN(Oracle)定义规范,由Apache Tomcat团队实现
JSTL可以帮助我们实现表格的循环,判断,数据的迭代等功能。
### JSTL下载与安装
el表达式,不需要下载任何的Jar包,这是因为现版本的jsp内置el表达式的实现,但是JSTL就需要下载Jar包并安装到项目中。
下载地址:[http://tomcat.apache.org/](http://tomcat.apache.org/)
JSTL 1.2.5组件介绍:
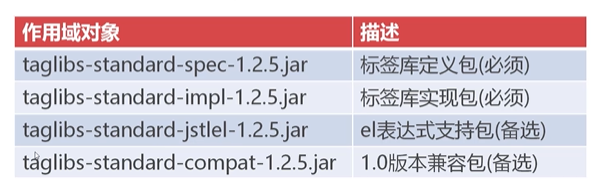
需要下载的是一个spec的包,一个是impl包,剩下的包,el的包是为了支持el表达式,现在el已经内置标签库了,所以不需要下载导入即可使用。第四个jar包是为了兼容1.0以下的包而使用的 我们现在使用的是1.2.5因此无需引入。
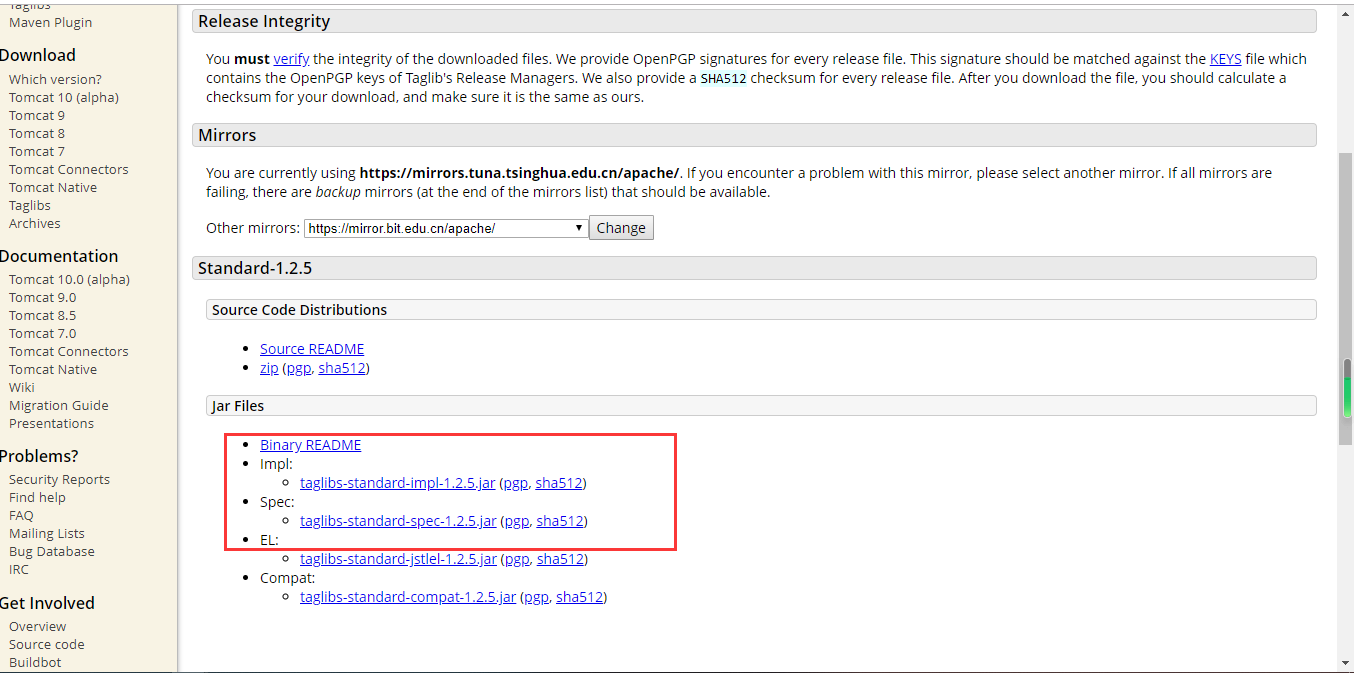
**安装JSTL**
JSTL的两种安装方式:
1. 将Jar文件复制到工程的/WEB-INF/lib目录下(对单体项目进行设置-推荐)
2. 将Jar文件复制到Tomcat安装目录的lib目录(全局设置)
### JSTL的标签库
JSTL按功能划分,可分为五类标签库:
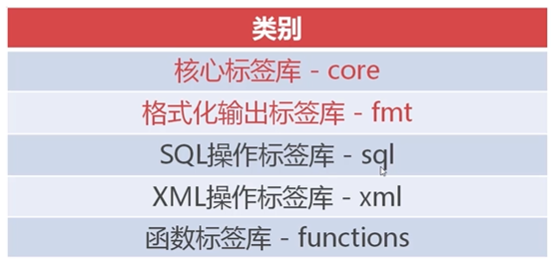
除了头两种,剩下的已经不使用了,因为在Java中提供了更好的支持。
**引用JSTL核心库**
核心标签库,提供了JSTL的基础功能,引用时需要在页面上引入该核心库
~~~
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
~~~
### JSTL判断标签
JSTL核心库提供了两组判断的标签:
* `<c:if>`用于单分支判断
* `<c:choose>`、`<c:when>`、`<c:otherwise>`用于多分支判断
~~~
@WebServlet("/jstl")
public class JstlServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public JstlServlet() {
super();
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setAttribute("score", 58);
request.setAttribute("grade", "B");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/core.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
}
~~~
~~~
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!-- 在Java或者JSP文件中输入 Alt + / 可出现智能提示 -->
<!-- uri指定使用哪个标签库,prefix指定使用时的前缀,prefix属性的值是可以改变的,只不过我们一般习惯用c表示。 -->
<%@ taglib uri = "http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix = "c" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>${requestScope.score}</h1>
<!-- 简单判断:test属性中填写true或false,用于决定c:if中的HTML语句是否输出 -->
<c:if test = "${score >= 60 }">
<h1 style = "color:green">恭喜,你已通过测试</h1>
</c:if>
<c:if test = "${score < 60 }">
<h1 style = "color:red">对不起,再接再厉</h1>
</c:if>
<!-- 复杂判断:choose when otherwise -->
${grade }
<c:choose>
<!-- 注意单引号,在JSTL中可以使用等号进行字符串的判断 -->
<c:when test="${grade == 'A'}">
<h2>你很优秀</h2>
</c:when>
<c:when test="${grade == 'B' }">
<h2>不错呦</h2>
</c:when>
<c:when test="${grade == 'C' }">
<h2>水平一般,需要提高</h2>
</c:when>
<c:when test = "${grade == 'D'}">
<h2>需要努力啦,不要气馁</h2>
</c:when>
<c:otherwise>
<h2>一切随缘吧</h2>
</c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
</body>
</html>
~~~
### JSTL遍历标签
`<c:forEach>`标签用于遍历集合(Collection)中的每一个对象。
~~~
public class Company {
private String cname;
private String url;
public Company(String cname , String url) {
this.cname = cname;
this.url = url;
}
public String getCname() {
return cname;
}
public void setCname(String cname) {
this.cname = cname;
}
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
}
~~~
~~~
@WebServlet("/jstl")
public class JstlServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public JstlServlet() {
super();
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setAttribute("score", 58);
request.setAttribute("grade", "B");
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new Company("腾讯" , "www.tencent.com"));
list.add(new Company("百度" , "www.baidu.com"));
list.add(new Company("渡课网" , "www.dodoke.com"));
request.setAttribute("companys", list);
request.getRequestDispatcher("/core.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
}
~~~
~~~
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<!-- 在Java或者JSP文件中输入 Alt + / 可出现智能提示 -->
<!-- uri指定使用哪个标签库,prefix指定使用时的前缀,prefix属性的值是可以改变的,只不过我们一般习惯用c表示。 -->
<%@ taglib uri = "http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix = "c" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>${requestScope.score}</h1>
<!-- test属性中填写true或false,用于决定c:if中的HTML语句是否输出 -->
<c:if test = "${score >= 60 }">
<h1 style = "color:green">恭喜,你已通过测试</h1>
</c:if>
<c:if test = "${score < 60 }">
<h1 style = "color:red">对不起,再接再厉</h1>
</c:if>
<!-- choose when otherwise -->
${grade }
<c:choose>
<!-- 注意单引号,在JSTL中可以使用等号进行字符串的判断 -->
<c:when test="${grade == 'A'}">
<h2>你很优秀</h2>
</c:when>
<c:when test="${grade == 'B' }">
<h2>不错呦</h2>
</c:when>
<c:when test="${grade == 'C' }">
<h2>水平一般,需要提高</h2>
</c:when>
<c:when test = "${grade == 'D'}">
<h2>需要努力啦,不要气馁</h2>
</c:when>
<c:otherwise>
<h2>一切随缘吧</h2>
</c:otherwise>
</c:choose>
<!-- forEach标签用于遍历集合
List companys = (List)request.getAttribute("companys")
for(Company c : companys){
out.print("...")
}
items 代表循环的数据源
var = c 指的是每一次循环得到的变量都会赋值给c
idx = index 循环的索引,但是索引值还是需要通过以下的index属性来获取
idx.index属性代表循环的索引值(0开始)
-->
<c:forEach varStatus="idx" items = "${requestScope.companys }" var = "c">
<h2 style="color:green">${idx.index + 1}-${c.cname }-${c.url }</h2>
</c:forEach>
</body>
</html>
~~~
### fmt格式化标签库
fmt格式化标签库可以使数据按照我们设想的格式进行输出。
它的引用地址为:
~~~
http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt
~~~
在这个标签库中,主要学习两种格式化语句:
**格式化日期标签**
`<fmt:formateDate value="" pattern="">`
**格式化数字标签**
`<fmt:formatNumber value="" pattern="">`
~~~
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" prefix="fmt" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Insert title here</title>
</head>
<body>
<%
//就在当前页面设置数据源,不再创建servlet了
request.setAttribute("amt", 1987654.326);
request.setAttribute("now", new java.util.Date());
request.setAttribute("html", "<a href='index.html'>index</a>");
request.setAttribute("nothing", null);
%>
<h2>${now }</h2>
<!--
formatDate pattern
yyyy - 四位年
MM - 两位月
dd - 两位日
HH - 24小时制
hh - 12小时制
mm - 分钟
ss - 秒数
SSS - 毫秒
-->
<h2>
<!-- value指原始的数据值,pattern表示转换的格式 -->
<fmt:formatDate value="${requestScope.now }" pattern="yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒 SSS毫秒" />
</h2>
<h2>${amt }</h2>
<h2>¥<fmt:formatNumber value = "${amt }" pattern="0,000.00"></fmt:formatNumber>元</h2>
<!-- 设置输出方式 -->
<h2>null默认值:<c:out value="${nothing }" default="无"></c:out> </h2>
<!-- 设置输出时是否转义 -->
<h2><c:out value="${ html}" escapeXml="true"></c:out></h2>
</body>
</html>
~~~
## 综合训练
通常在进行实际项目的开发时,前端工程师会发送给我们一个静态的页面,而我们要做的就是将这样的静态页面变为动态页面。
静态演示Demo下载地址:链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1HFMuCGeg5tox-1MWzGs_vQ 提取码: 2j2z
实例:
~~~
public class Employee {
private Integer empno;
private String ename;
private String department;
private String job;
private Float salary;
public Employee(Integer empno, String ename, String department, String job, Float salary) {
super();
this.empno = empno;
this.ename = ename;
this.department = department;
this.job = job;
this.salary = salary;
}
public Integer getEmpno() {
return empno;
}
public void setEmpno(Integer empno) {
this.empno = empno;
}
public String getEname() {
return ename;
}
public void setEname(String ename) {
this.ename = ename;
}
public String getDepartment() {
return department;
}
public void setDepartment(String department) {
this.department = department;
}
public String getJob() {
return job;
}
public void setJob(String job) {
this.job = job;
}
public Float getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(Float salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}
~~~
~~~
@WebServlet("/list")
public class ListServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public ListServlet() {
super();
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext context = request.getServletContext();
if(context.getAttribute("employees") == null) {
List list = new ArrayList();
Employee emp = new Employee(7731 , "刘志敏" , "市场部" , "客户代表" , 10000f);
list.add(emp);
list.add(new Employee(8871 , "张倩" , "研发部" , "运维工程师" , 8000f));
context.setAttribute("employees", list);
}
request.getRequestDispatcher("/employee.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
}
~~~
~~~
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=utf-8"%>
<%@ taglib uri = "http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix = "c" %>
<%@ taglib uri = "http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" prefix = "fmt" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1">
<title>员工列表</title>
<link href="css/bootstrap.css" type="text/css" rel="stylesheet"></link>
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery-1.11.1.min.js"></script>
<script type="text/javascript" src="js/bootstrap.js"></script>
<style type="text/css">
.pagination {
margin: 0px
}
.pagination > li > a, .pagination > li > span {
margin: 0 5px;
border: 1px solid #dddddd;
}
.glyphicon {
margin-right: 3px;
}
.form-control[readonly] {
cursor: pointer;
background-color: white;
}
#dlgPhoto .modal-body{
text-align: center;
}
.preview{
max-width: 500px;
}
</style>
<script>
$(function () {
$("#btnAdd").click(function () {
$('#dlgForm').modal()
});
})
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<h1 style="text-align: center">dodoke员工信息表</h1>
<div class="panel panel-default">
<div class="clearfix panel-heading ">
<div class="input-group" style="width: 500px;">
<button class="btn btn-primary" id="btnAdd"><span class="glyphicon glyphicon-zoom-in"></span>新增
</button>
</div>
</div>
<table class="table table-bordered table-hover">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>序号</th>
<th>员工编号</th>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>部门</th>
<th>职务</th>
<th>工资</th>
<th> </th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<c:forEach items = "${applicationScope.employees}" var = "emp" varStatus="idx" >
<tr>
<td>${idx.index + 1}</td>
<td>${emp.empno }</td>
<td>${emp.ename }</td>
<td>${emp.department }</td>
<td>${emp.job }</td>
<td style="color: red;font-weight: bold">¥<fmt:formatNumber value = "${emp.salary }" pattern="0,000.00" ></fmt:formatNumber></td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<!-- 表单 -->
<div class="modal fade" tabindex="-1" role="dialog" id="dlgForm">
<div class="modal-dialog" role="document">
<div class="modal-content">
<div class="modal-header">
<button type="button" class="close" data-dismiss="modal" aria-label="Close"><span aria-hidden="true">×</span>
</button>
<h4 class="modal-title">新增员工</h4>
</div>
<div class="modal-body">
<form action="/employee/create" method="post" >
<div class="form-group">
<label >员工编号</label>
<input type="text" name="empno" class="form-control" id="empno" placeholder="请输入员工编号">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label >员工姓名</label>
<input type="text" name="ename" class="form-control" id="ename" placeholder="请输入员工姓名">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>部门</label>
<select id="dname" name="department" class="form-control">
<option selected="selected">请选择部门</option>
<option value="市场部">市场部</option>
<option value="研发部">研发部</option>
<option value="后勤部">后勤部</option>
</select>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>职务</label>
<input type="text" name="job" class="form-control" id="sal" placeholder="请输入职务">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label >工资</label>
<input type="text" name="salary" class="form-control" id="sal" placeholder="请输入工资">
</div>
<div class="form-group" style="text-align: center;">
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">保存</button>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div><!-- /.modal-content -->
</div><!-- /.modal-dialog -->
</div><!-- /.modal -->
</body>
</html>
~~~
~~~
@WebServlet("/create")
public class CreateServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public CreateServlet() {
super();
}
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
String empno = request.getParameter("empno");
String ename = request.getParameter("ename");
String department = request.getParameter("department");
String job = request.getParameter("job");
String salary = request.getParameter("salary");
System.out.println(empno);
Employee emp = new Employee(Integer.parseInt(empno) , ename , department , job , Float.parseFloat(salary));
ServletContext context = request.getServletContext();
List employees = (List)context.getAttribute("employees");
employees.add(emp);
context.setAttribute("employees", employees);
request.getRequestDispatcher("/employee.jsp").forward(request, response);
}
}
~~~
